📐 "First 50 Enterprise Queries Get Custom 3D Warehouse Design" Plan

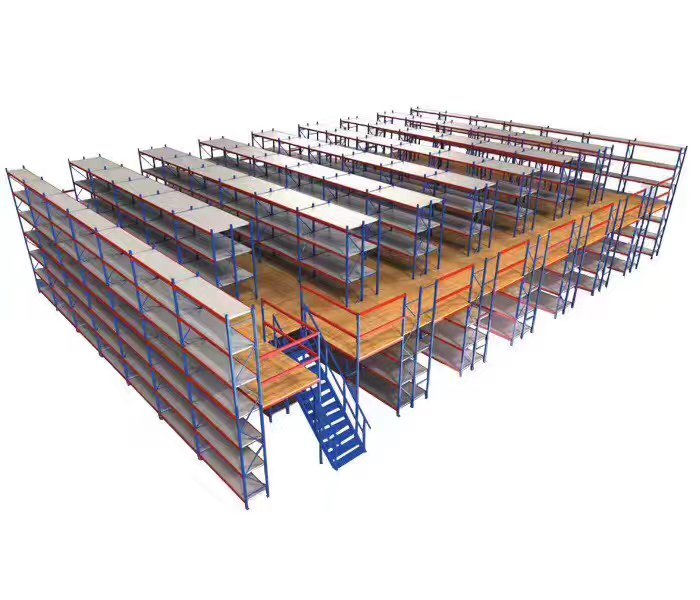
Solving Your Cold Storage Space Crunch with a Custom Mezzanine Racking Layout
The relentless pressure of the “cold storage space crunch” is a formidable challenge confronting logistics managers and business owners across the globe. This crisis transcends mere inconvenience; it represents a severe operational and financial bottleneck where exponential growth collides with finite physical space. The conventional solution of constructing new cold storage facilities is often a prohibitive venture, burdened by astronomical capital expenditure, protracted timelines, and complex regulatory hurdles. A more intelligent, immediately actionable strategy exists: the strategic deployment of a meticulously engineered mezzanine racking for cold storage.
This approach transforms the costly, underutilized vertical airspace within an existing facility into a high-density, highly organized storage and operational platform. The pivotal differentiator between a mere spatial expansion and a transformative operational upgrade lies in one critical factor: customization. A generic, off-the-shelf mezzanine racking for cold storage solution will inevitably fall short. True efficiency is only unlocked through a custom mezzanine racking layout that is intrinsically woven into the unique fabric of a facility’s workflow, material handling protocols, and long-term strategic goals.
This in-depth exploration will dissect the multifaceted process of conceptualizing, engineering, and implementing a superior mezzanine racking for cold storage system, demonstrating its unparalleled capacity to not only resolve space constraints but to fundamentally elevate the entire cold chain operation.

H2: Deconstructing the True Cost of Inefficient Cold Storage Space
To fully appreciate the transformative impact of a mezzanine racking for cold storage system, one must first conduct a rigorous audit of the exorbitant costs associated with spatial inefficiency. In the thermally demanding environment of a cold storage warehouse, waste is magnified, and operational shortcomings carry a significantly heavier price tag.
H3: The Financial Drain of Wasted Cubic Air and Refrigeration Inefficiency
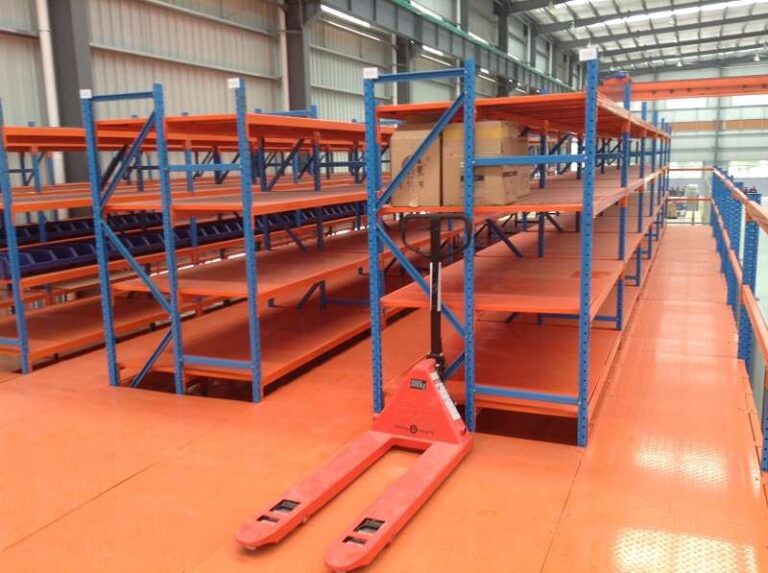
The most glaring, yet frequently overlooked, financial drain is the systematic refrigeration of empty, unused cubic air. A facility boasting 10-meter high ceilings that utilizes only 4-meter high conventional racking is, in effect, consuming vast amounts of electricity to cool 6 meters of unproductive void. Refrigeration constitutes the single largest operational expenditure for any cold storage operation, and cooling this dead space is tantamount to incinerating capital. A strategically implemented mezzanine racking for cold storage system is engineered to eradicate this inefficiency. By creating a second or even third tier of usable space within the existing building envelope, it dramatically increases the storage density, thereby distributing the fixed cost of refrigeration across a vastly greater number of pallet positions.
This action directly and substantially lowers the cost per stored pallet, delivering a continuous and significant reduction in operational overhead. The strategic implementation of mezzanine racking for cold storage is, therefore, a direct and powerful intervention against energy waste.
H3: Workflow Congestion, Labor Inefficiency, and the Human Factor
Spatial constraints inevitably manifest as workflow congestion. In a poorly optimized layout, material handling equipment navigates excessively long and convoluted travel paths, while personnel expend valuable time and energy retrieving items. Within the harsh environment of a -25°C freezer, every additional minute spent by an employee is not merely a productivity loss; it presents a serious human resource challenge and elevates safety risks. A disorganized, cramped space often leads to more frequent door openings as workers struggle to locate items, causing damaging temperature fluctuations and a further surge in energy consumption.
A custom mezzanine racking layout is specifically designed to dismantle these inefficiencies. It facilitates the logical zoning of inventory, segregates different operational functions onto distinct levels, and creates streamlined, purpose-built pathways for both personnel and machinery. This thoughtful integration of mezzanine racking for cold storage into the operational blueprint minimizes travel time, accelerates order fulfillment, and fosters a safer, more productive working environment.
H3: The Perils of Overcrowding: Safety, Compliance, and Inventory Integrity
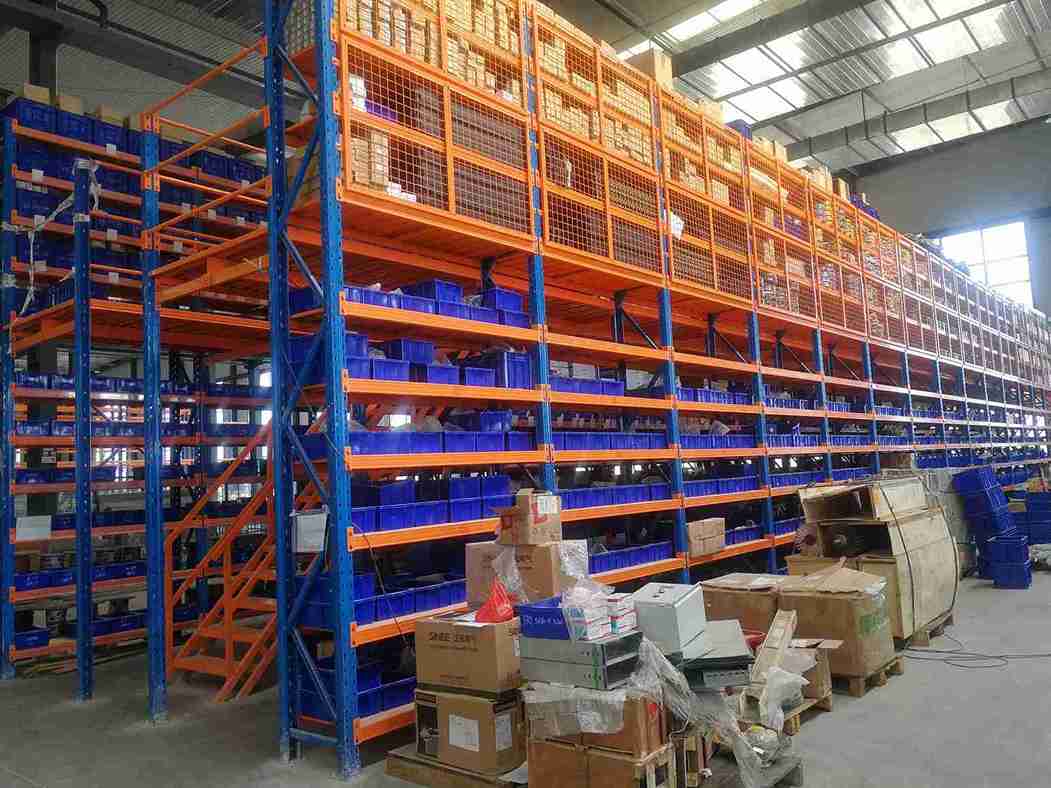
When floor space is exhausted, the inevitable result is dangerous overcrowding. Aisles become obstructed, fire exits are inadvertently blocked, and clear access paths are compromised. This creates a high-risk environment for personnel and jeopardizes the integrity of the stored inventory. Furthermore, such conditions make it nearly impossible to maintain compliance with stringent health and safety regulations and food safety protocols like HACCP and GDP. A professionally engineered mezzanine racking for cold storage system provides the structured, dedicated space required to eliminate this hazardous clutter. It ensures the maintenance of clear egress routes, facilitates proper air circulation around stored goods, and establishes a organized, audit-ready environment that underpins both safety and regulatory compliance.

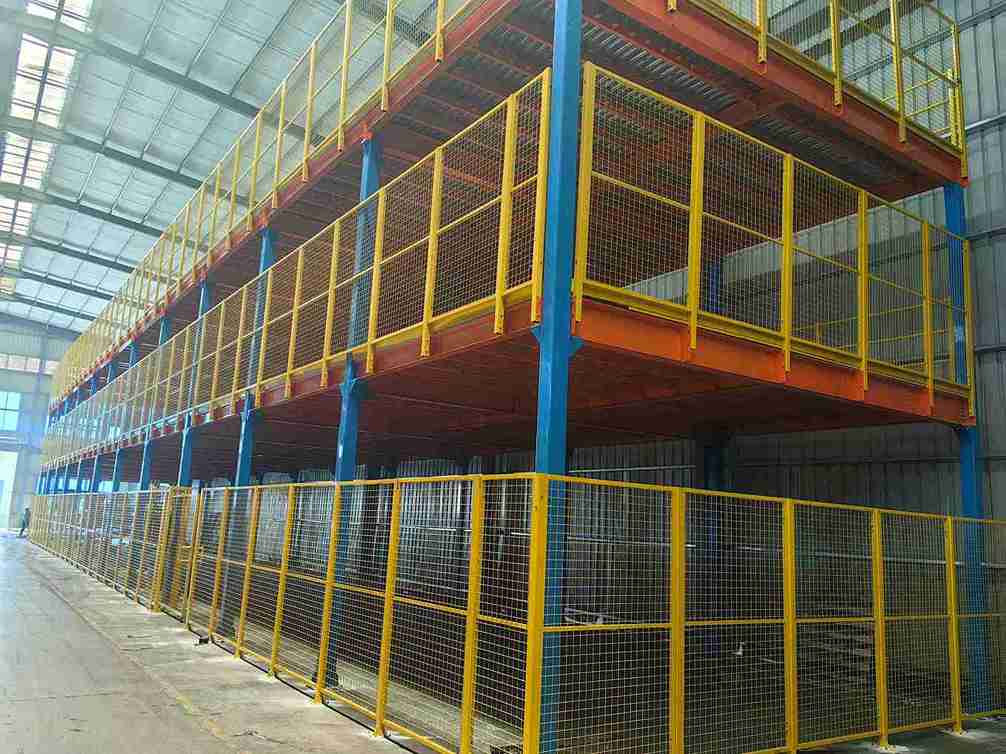
H2: The Unmatched Superiority of Custom Mezzanine Racking for Cold Storage
While several alternatives exist for augmenting storage capacity, a purpose-built mezzanine racking for cold storage system represents a category of its own. It is not a simple storage product; it is an integrated, structural asset that redefines the operational potential of a facility.
H3: The Financial Imperative: Mezzanine Racking vs. New Construction
The construction of a new greenfield cold storage facility is a capital-intensive undertaking that can easily escalate into a multi-year, multi-million-dollar project. This process encompasses land acquisition, architectural design, lengthy construction phases, and the installation of massive, complex refrigeration systems. In stark contrast, a project centered on mezzanine racking for cold storage is typically completed within a matter of weeks or months, requiring a fraction of the financial outlay.
The return on investment is consequently dramatically accelerated. This approach leverages the existing building shell, insulation, and refrigeration infrastructure, making it the most fiscally prudent and strategically agile method for achieving rapid and substantial capacity expansion. The economic argument for investing in a robust mezzanine racking for cold storage system is overwhelmingly compelling.
H3: Beyond Simple Racking: The Multi-Level Workflow Revolution
The strategy of merely inserting more conventional racking into an already cramped floorplan is a fundamentally flawed and short-sighted endeavor. This approach often exacerbates aisle congestion, diminishes lighting efficiency, and fails to address the root causes of workflow inefficiency. A mezzanine racking for cold storage system, however, enables a revolutionary multi-level operational model. The ground floor can be exclusively dedicated to high-volume, pallet-in/pallet-out activities, seamlessly serviced by forklifts.
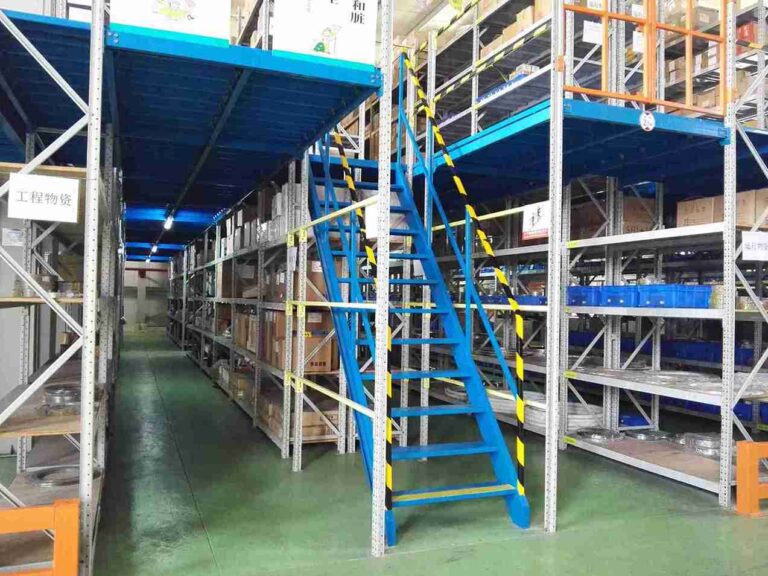
The mezzanine level, accessible via integrated lifts or staircases, can be transformed into a high-efficiency order picking zone, a storage area for slow-moving goods, or a dedicated space for value-added services like kitting and labeling. This vertical segregation of distinct functions, enabled by a custom mezzanine racking layout, is a proven game-changer for holistic workflow optimization and throughput enhancement.

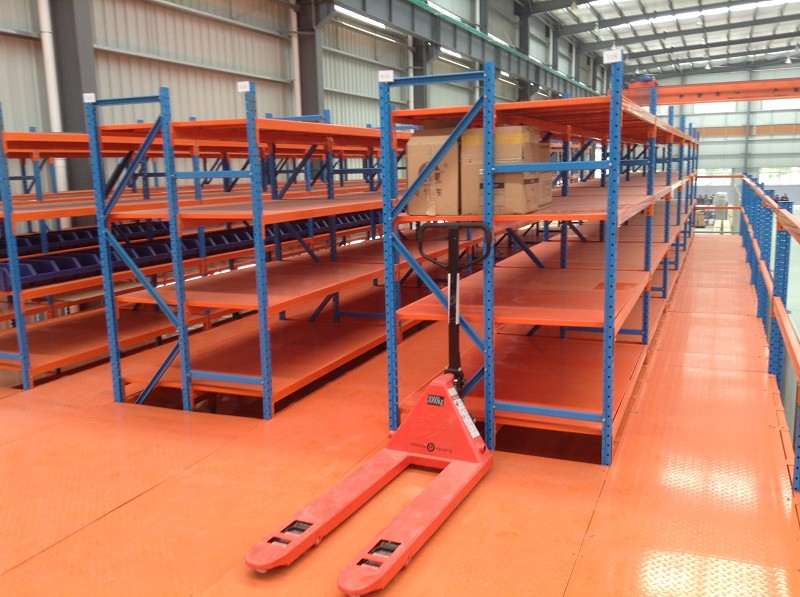
H2: The Science of Engineering: Building a Mezzanine for Extreme Environments
The successful implementation of a mezzanine racking for cold storage system is fundamentally dependent on specialized engineering. A standard warehouse mezzanine is utterly unsuitable for the relentless physical demands of a cold storage environment. This application requires a deep understanding of material science, thermal dynamics, and structural integrity under duress.
H3: The Criticality of Low-Temperature Steel Alloys and Specialized Coatings
Standard structural steel undergoes a dangerous transition in sub-zero temperatures, becoming increasingly brittle and losing its fracture resistance. The use of such material in a -30°C freezer would pose an unacceptable risk of catastrophic failure. Every component of a dedicated mezzanine racking for cold storage must be fabricated from certified low-temperature carbon steel alloys, which are specifically engineered to retain their ductility and impact toughness at temperatures as low as -40°C and beyond.
Furthermore, all structural elements require application of specialized, cold-tolerant epoxy coatings that resist chipping, cracking, and corrosion in high-humidity environments, ensuring the long-term structural soundness and safety of the mezzanine racking for cold storage installation.
H3: Combating Thermal Bridging and Condensation with Advanced Engineering
Thermal bridging is a pervasive and costly issue in cold storage facilities. It occurs when highly conductive materials, like standard steel, create a pathway for thermal energy to flow from the outside to the inside of the refrigerated space. In the context of a mezzanine racking for cold storage, unmitigated thermal bridging at the connection points between the mezzanine structure and the building can lead to significant energy loss and, more critically, the formation of condensation and ice on the steel members.
To combat this, the design of a mezzanine racking for cold storage must incorporate proprietary thermal break technology. This includes the use of high-density polymer pads and insulated brackets at all structural interfaces, effectively isolating the mezzanine from the building structure and preserving the thermal integrity of the envelope. This sophisticated engineering is non-negotiable for an efficient and safe mezzanine racking for cold storage system.
H3: Decking, Flooring, and Safety Systems for a Harsh Climate
The selection of decking and flooring for a mezzanine racking for cold storage platform is a critical safety and performance decision. Solid sheet metal decking can become treacherously icy and slippery. The industry best practice recommends the use of heavy-duty open-grid steel decking, which permits natural and unrestricted circulation of cold air, prevents the accumulation of snow and ice, and provides superior underfoot traction for personnel.
For deck levels that require a solid surface for cart traffic or the handling of small items, the integration of specialized, cold-rated anti-slip flooring systems is essential. Additionally, the design must include robust perimeter guarding, safety gates, and strategically placed access points to ensure complete compliance with all occupational health and safety standards for a mezzanine racking for cold storage installation.
H2: The Blueprint for Operational Excellence: Co-Designing the Custom Mezzanine Layout
The term “custom” is the cornerstone of a successful mezzanine racking for cold storage project. It represents a collaborative, consultative process aimed at delivering a solution that is perfectly symbiotic with the client’s unique operational ecosystem.
H4: Phase 1: Comprehensive Workflow and Process Auditing
The foundational phase of any mezzanine racking for cold storage project is an exhaustive, on-site audit of current and projected operations. This due diligence goes far beyond simple physical dimensions. It involves a granular analysis of SKU velocity profiles, detailed mapping of all picking and put-away pathways, assessment of material handling equipment, and a thorough understanding of integration points with existing or planned automation systems like AGVs or automated conveyor belts. This deep dive is indispensable for informing the design of a truly optimized custom mezzanine racking layout.
H4: Phase 2: Dynamic 3D Modeling and Virtual Flow Simulation
Leveraging state-of-the-art CAD and simulation software, the proposed mezzanine racking for cold storage design is brought to life as an interactive 3D model. This virtual twin of the facility allows stakeholders to conduct a immersive “walk-through” of the future operation. More importantly, it enables engineers to run dynamic material flow simulations, identifying and rectifying potential bottlenecks, traffic conflicts, or inefficiencies long before any physical installation commences. This proactive, digital-validation step is crucial for ensuring the proposed custom mezzanine racking layout will perform as intended in the real world.
H4: Phase 3: Meticulous Engineering and Regulatory Adherence
Upon final approval of the conceptual design, the project transitions into the detailed engineering phase. Certified structural engineers produce comprehensive fabrication and installation drawings. This stage also involves ensuring the entire design for the mezzanine racking for cold storage adheres strictly to all applicable local building codes, seismic regulations, and industry-specific safety standards, such as those from ANSI and other relevant bodies. This rigorous documentation guarantees both the safety and the legal compliance of the installation.
H2: Seamless Integration: The Mezzanine in an Automated Warehouse Ecosystem
A modern mezzanine racking for cold storage system should not function as an isolated entity. It must be a fully integrated, synergistic component of a broader automated or semi-automated warehouse ecosystem.
H3: Enabling a Multi-Level AGV and AMR Workflow
A critical question in multi-level design is the vertical transportation of goods. The solution lies in the integration of specialized material lifts and vertical reciprocating conveyors (VRCs) that are themselves engineered for reliable operation in cold storage environments. These automated vertical transport systems can be seamlessly interfaced with a fleet of AGVs or AMRs, creating a continuous, hands-off material flow between levels. Pallets or totes are automatically delivered to the lift by a ground-level robot, transported vertically, and received by another robot on the mezzanine level for final put-away, making the mezzanine racking for cold storage a dynamic part of the automated workflow.
H3: Synergistic Coexistence with Pallet Racking and AS/RS
The structural design of a mezzanine racking for cold storage system often allows it to be supported by, and integrated with, the facility’s existing or new selective pallet racking. This creates a highly efficient, hybrid storage structure. Furthermore, the clear-span space beneath the mezzanine deck is ideal for housing high-density storage solutions like narrow aisle racking or even a fully-fledged Automated Storage and Retrieval System (AS/RS), maximizing the utility of every single cubic meter of available space. This holistic approach to integrating mezzanine racking for cold storage with other systems is the hallmark of a world-class storage solution.
H2: Quantifying the Investment: A Detailed Return on Investment Analysis
Investing in a mezzanine racking for cold storage system is a significant strategic decision, and its financial justification must be clear, comprehensive, and compelling.
H3: Calculating Tangible Gains in Storage Capacity and Operational Value
The most direct component of the ROI calculation is the quantifiable gain in storage capacity. For instance, if a mezzanine racking for cold storage project adds 2,000 square meters of usable space, and each pallet position generates a specific value in monthly revenue or saved external storage costs, the annual financial benefit is straightforward to project. This must be coupled with the calculated savings from the reduced refrigeration cost per pallet, a direct result of the increased storage density. The financial model for the mezzanine racking for cold storage must clearly articulate these direct gains.
H3: Accounting for the Substantial “Soft Cost” Savings
The true ROI of a mezzanine racking for cold storage extends far beyond pure storage metrics. It encompasses the substantial savings from a 25-40% reduction in order picking time, the dramatic improvement in order accuracy, the reduction in product damage from a more organized environment, and the decrease in worker compensation incidents due to a safer, less congested workspace. Furthermore, the ability to handle increased sales volume without the delay and cost of new construction represents a significant strategic advantage. A professional ROI analysis for a mezzanine racking for cold storage system will meticulously quantify these “soft cost” benefits to present a complete picture of the investment’s value.
H2: A Concrete Illustration: Transforming a Frozen Food Distributor’s Operation
Consider the case of a large frozen food distributor in Thailand, whose -22°C freezer was operating at 170% of its intended capacity, forcing reliance on expensive and logistically challenging external storage. The implementation of a sophisticated, two-tier mezzanine racking for cold storage system was the definitive solution.
Ground Floor Configuration: Reserved for inbound receiving and high-throughput bulk pallet storage.
First Mezzanine Level: Engineered as a multi-level pick module for efficient case picking, with integrated conveyors leading directly to the dispatch area.
Second Mezzanine Level: Dedicated to the storage of slow-moving products and packaging materials.
The outcome of this tailored mezzanine racking for cold storage project was a 150% increase in effective storage capacity, a 45% reduction in order cycle times, and the complete elimination of external storage leases, resulting in a full project payback in under 16 months. This case exemplifies the transformative power of a well-executed mezzanine racking for cold storage strategy.
H2: The Installation Protocol: Ensuring Minimal Operational Disruption
A paramount concern for any live cold storage operation is the potential disruption caused by a construction project. A professional installation of mezzanine racking for cold storage is meticulously planned to minimize this impact.
H3: The Pre-Fabrication Advantage and Just-in-Time Logistics
A key to a swift and clean installation is the principle of off-site pre-fabrication. The entire mezzanine racking for cold storage structure is manufactured, drilled, and painted in a controlled factory setting. Components are then delivered to the site on a strict just-in-time schedule, ready for immediate assembly. This methodology drastically reduces on-site labor time, minimizes waste, and limits the potential for contamination within the sensitive cold storage environment.
H3: Phased Implementation and Cold-Work Expertise
The installation team works in close collaboration with the client’s operations managers to develop a detailed phased implementation plan. This strategy allows the installation of the mezzanine racking for cold storage to proceed in designated zones while the remainder of the warehouse continues to function normally. Furthermore, the installation crews are specially trained and equipped with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) for working efficiently and safely in cold environments, ensuring their well-being and the integrity of the temperature-controlled space.
H2: Ensuring Longevity: Maintenance and Durability in a Demanding Environment
A high-quality mezzanine racking for cold storage system is a long-term capital asset designed for decades of reliable service. The combination of low-temperature steel and advanced coating systems ensures exceptional resistance to corrosion and the physical stresses of thermal cycling. Maintenance requirements are minimal and primarily consist of scheduled visual inspections to check the tightness of bolts and the condition of structural members, guaranteeing that the investment in mezzanine racking for cold storage continues to deliver a safe and outstanding performance for its entire lifecycle.
H2: Conclusion: Taking the Definitive Step Toward a Crunch-Free Future
The challenge of the “cold storage space crunch” is not an insurmountable obstacle. The most powerful and economically sound solution lies in the strategic and courageous utilization of the vertical potential lying dormant within existing facilities. A custom mezzanine racking layout, conceived through a collaborative design process, engineered with precision for harsh environments, and seamlessly integrated into operational workflows, stands as the most effective instrument for achieving transformative gains in capacity, efficiency, and profitability.
It is the definitive answer for businesses determined to build a more resilient, agile, and competitive cold chain operation. The journey toward this optimized future begins with a professional consultation and a detailed assessment of your specific operational landscape.
H2: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the typical project timeline from initial design to a fully operational cold storage mezzanine racking system?
A complete project for a mezzanine racking for cold storage system typically follows a 14 to 22-week timeline, contingent on the project’s scale and complexity. This encompasses a 3-5 week period for detailed design and engineering, a 9-13 week window for off-site fabrication, and a final 2-4 week phase for on-site installation and commissioning. The phased installation strategy is specifically designed to ensure core warehouse activities can continue with minimal interruption.
2. Can a mezzanine racking for cold storage be retrofitted into an existing blast freezer without compromising its thermal integrity?
Yes, this is a standard and core competency for specialist engineers. The design and installation of mezzanine racking for cold storage in existing chambers employs non-penetrating connection methods wherever structurally feasible. When direct connections to the building are necessary, engineered thermal break solutions, including specialized isolation pads and insulated brackets, are systematically used to prevent thermal bridging and preserve the freezer’s thermal envelope and energy efficiency.
3. How are dynamic loads from automation and active workstations accounted for in the structural design?
The structural engineering for a mezzanine racking for cold storage system incorporates sophisticated analysis that transcends simple static load calculations. It includes dynamic load factoring for continuous foot traffic, the impact forces from manual pallet jacks, and the specific vibrational and point-load characteristics of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and automated conveyor systems. Designs are executed with substantial safety factors, often exceeding local building code mandates, to ensure a rigid, vibration-free, and safe platform for both storage and dynamic operational functions.
4. What are the critical fire safety and sprinkler system integration requirements for a multi-level mezzanine?
This is a non-negotiable aspect of the design process. The installation of a mezzanine racking for cold storage platform will alter the existing sprinkler head coverage pattern. The design process mandates coordination with licensed fire protection engineers to design a compliant sprinkler system for the new mezzanine level. This typically involves installing a dedicated sprinkler loop with strategically placed heads beneath the mezzanine deck to ensure complete coverage and full integration with the building’s primary fire suppression system.
5. What provisions are made for future expansion or reconfiguration of the mezzanine racking system?
Professional designs for mezzanine racking for cold storage prioritize future flexibility and scalability. Many systems are conceived with a modular architecture, allowing for future lateral expansion or the reconfiguration of racking modules on the deck level. During the initial design consultation for the mezzanine racking for cold storage, the client’s strategic growth plans are discussed to ensure the foundational structure possesses the inherent capacity to accommodate foreseeable future expansion needs, thereby protecting the long-term value of the investment.
Welcome to contact us, if you need warehouse rack CAD drawings. We can provide you with warehouse rack planning and design for free. Our email address is: jili@geelyracks.com